UNMET NEED
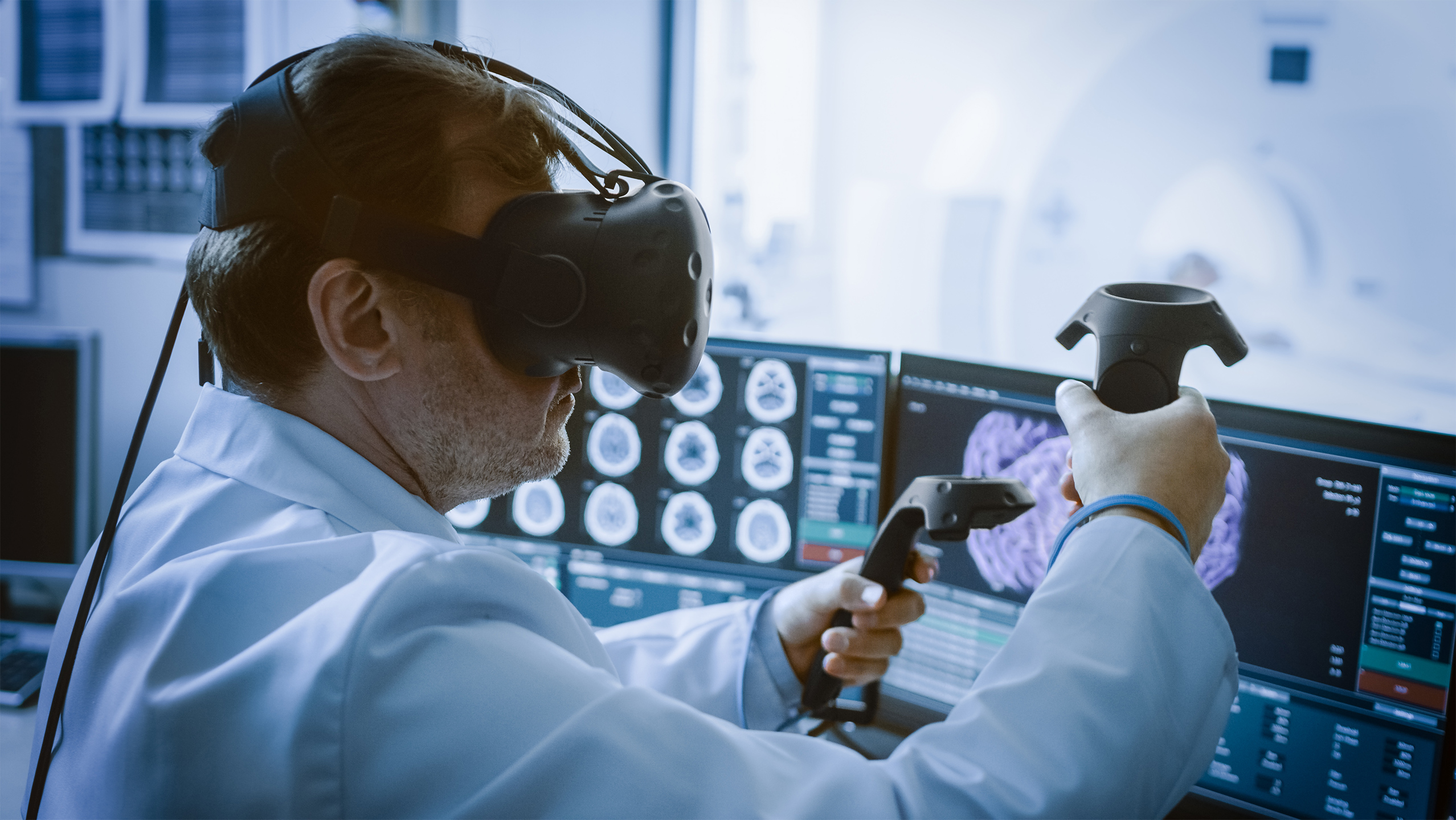
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure in which electrodes are implanted into the brain to send electrical signals to specific deep areas (e.g., subthalamic nucleus). It is used for the treatment of movement and psychiatric disorders including Parkinson’s disease such as, essential tremor, dystonia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, and epilepsy.
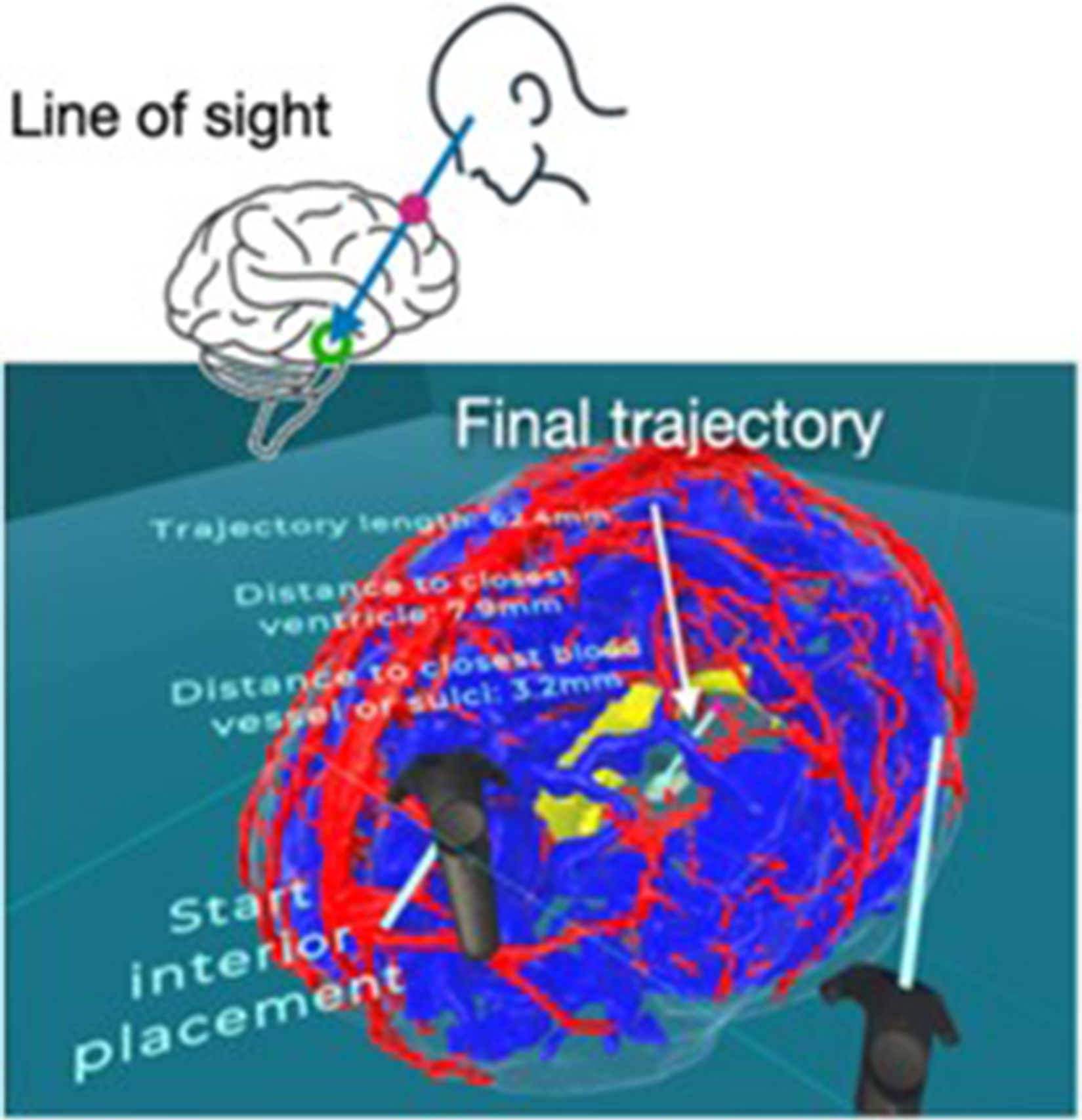
The success of the procedure depends heavily on the accurate placement of the electrode within the optimal therapeutic targets while avoiding vital structures that can cause surgical complications and adverse neurologic effects. The neurosurgeon conventionally uses a software platform showing multiple 2D cut planes of medical images and mentally determines the best implantation trajectory in the 3D brain structure. (i) This method requires a long training process, (ii) takes around 40min for each patient and (iii) is highly prone to human errors.